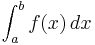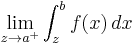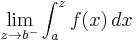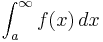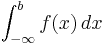Limits of integration
In calculus and mathematical analysis the limits of integration of the integral
of a Riemann integrable function f defined on a closed and bounded [interval] are the real numbers a and b.
Improper integrals
Limits of integration can also be defined for improper integrals, with the limits of integration of both
and
again being a and b. For an improper integral
or
the limits of integration are a and ∞, or −∞ and b, respectively.